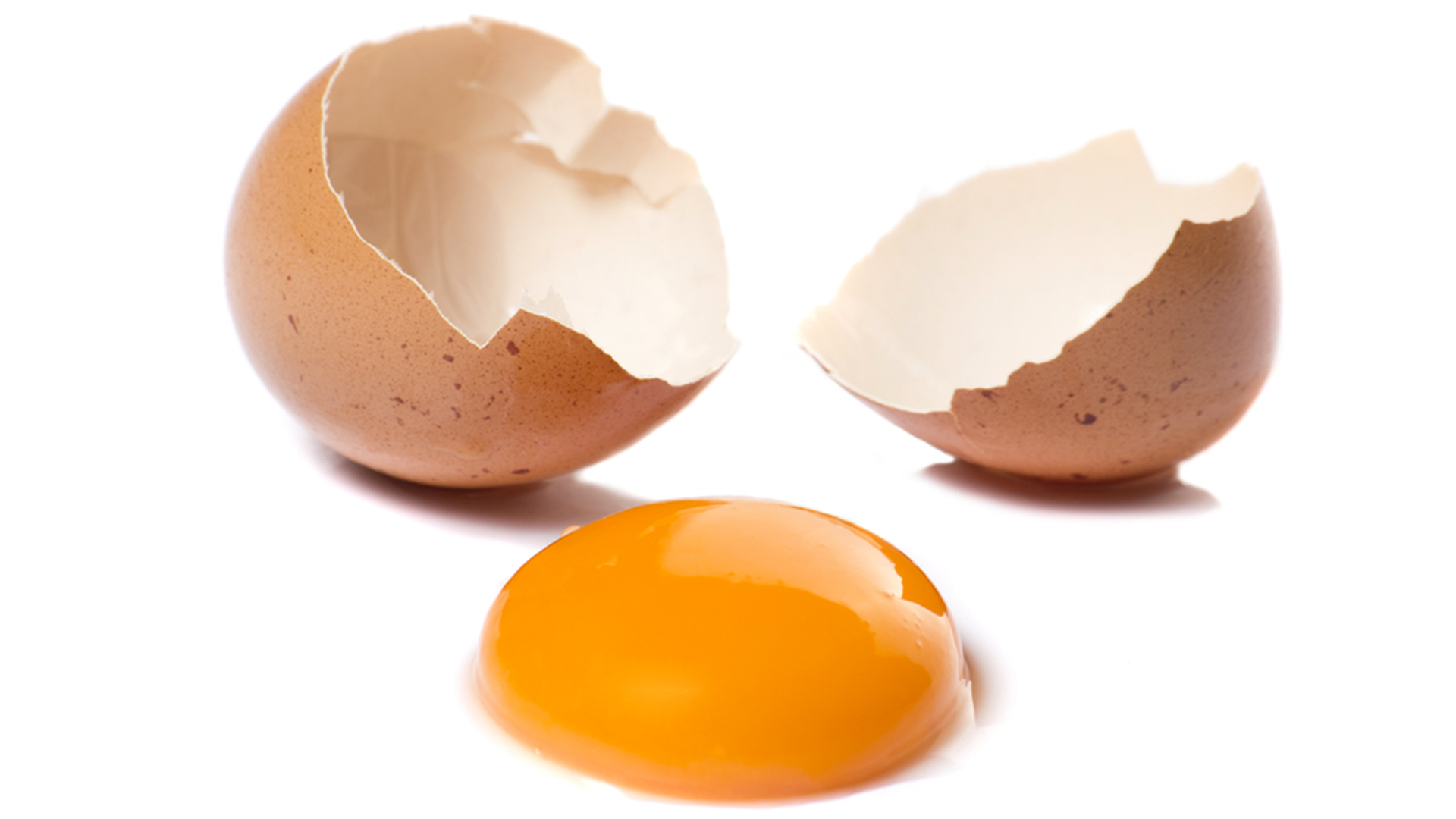
Eggshells are commonly discarded as waste after using the egg for cooking or baking. However, some people have started to explore the potential benefits of consuming eggshells due to their high calcium content and other essential minerals. While there are potential benefits to eating eggshells, it is important to understand the risks and consider proper preparation methods. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the potential benefits and risks associated with eating eggshells to help you make an informed decision.
Benefits of Eating Eggshells:
- Calcium Source: Eggshells are primarily composed of calcium carbonate, a highly absorbable form of calcium. Consuming eggshells can help meet your body’s calcium requirements, which is essential for maintaining healthy bones and teeth, supporting nerve function, and promoting proper muscle contractions.
- Mineral-Rich: In addition to calcium, eggshells contain small amounts of other minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. These minerals play crucial roles in various bodily functions, including nerve conduction, energy production, and maintaining electrolyte balance.
- Collagen Boost: Eggshells also contain collagen, a protein that provides structural support to the body. Consuming eggshells may help promote collagen production, which can benefit the health of your skin, joints, and connective tissues.
- Waste Reduction: By consuming eggshells, you can minimize waste and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle. Repurposing eggshells as a food source can reduce the environmental impact associated with waste disposal.
Risks and Considerations:
- Contamination: One of the primary risks of consuming eggshells is the potential for bacterial contamination. Eggshells may harbor harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella, which can cause food poisoning. Proper handling, cleaning, and preparation techniques are essential to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Pesticides and Chemicals: Commercially produced eggs may be exposed to pesticides or other chemicals. These substances can potentially transfer to the eggshells. It is important to choose organic or free-range eggs to reduce the risk of consuming harmful residues.
- Digestive Issues: Eggshells are primarily composed of calcium carbonate, which can be challenging for some individuals to digest. People with digestive conditions, such as acid reflux or sensitive stomachs, may experience discomfort or irritation after consuming eggshells. If you have any pre-existing digestive issues, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating eggshells into your diet.
- Allergies: While rare, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to eggshells. Symptoms can range from mild itching or rash to severe allergic reactions. If you have a known egg allergy, it is best to avoid consuming eggshells altogether.
Safe Preparation Methods:
To minimize the risks associated with consuming eggshells, it is crucial to follow proper preparation methods. Here are some guidelines to ensure safety:
- Clean and Sanitize: Before using eggshells, make sure to clean them thoroughly. Wash the eggshells with warm water and mild dish soap to remove any dirt, bacteria, or potential chemical residues. Rinse them thoroughly and allow them to air dry.
- Sterilize: To further reduce the risk of bacterial contamination, sterilize the eggshells by boiling them in water for around 5 minutes. This process helps eliminate any remaining bacteria on the shells’ surface.
- Crush or Powder: Once sterilized and cooled, crush the eggshells into fine powder using a mortar and pestle or a food processor. Grinding the eggshells into a powder makes them easier to consume and digest.
- Incorporate into Food: Add the crushed eggshells to your favorite foods or recipes. They can be mixed into smoothies, sprinkled over cereals or salads, or used as an ingredient in baked goods. Start with small amounts and gradually increase the quantity to allow your body to adjust.
- Store Properly: Store the crushed eggshells in an airtight container in a cool, dry place to maintain their freshness and prevent contamination.
Conclusion:
Eating eggshells can provide a potential source of calcium and other essential minerals, along with potential collagen-boosting benefits. However, it is crucial to understand and address the associated risks. Proper handling, cleaning, and preparation methods are vital to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination and ensure safety. If you have any pre-existing health conditions or concerns, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating eggshells into your diet. By considering the benefits and risks outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can make an informed decision about including eggshells in your dietary routine.